As the summer heat rolls in, many of us rely on air conditioners to keep us cool and comfortable indoors. But have you ever stopped to wonder how these remarkable machines actually work?
The Basics of Air Conditioning
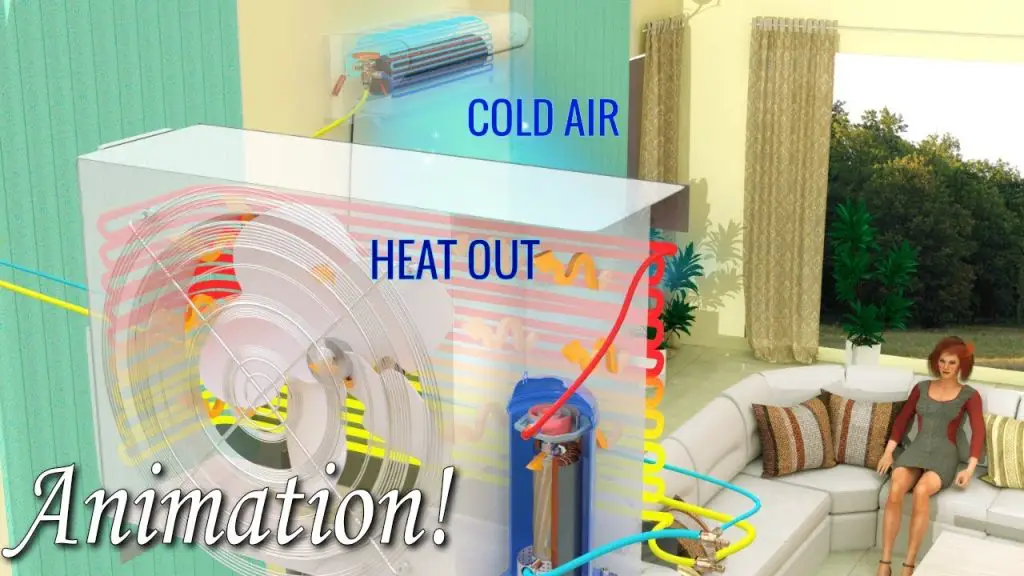
At its core, air conditioning is the process of removing warm air from an enclosed space and replacing it with cooler air. This is achieved through a combination of refrigeration principles and the circulation of air.
Key Components Of An Air Conditioner
Understanding how an air conditioner works starts with knowing its key components:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Refrigerant | Absorbs and releases heat as it circulates through the system. |
| Evaporator Coil | Where the refrigerant absorbs heat from indoor air, cooling it in the process. |
| Condenser Coil | Releases the heat absorbed by the refrigerant to the outside air. |
| Compressor | Pressurizes the refrigerant, raising its temperature and pressure. |
| Expansion Valve | Regulates the flow of the refrigerant into the evaporator coil. |

Credit: www.hitachiaircon.com
The Refrigeration Cycle
The operation of an air conditioner is based on the refrigeration cycle, which consists of four main processes:
- Compression: The refrigerant enters the compressor as a low-pressure gas and is compressed into a high-pressure gas, raising its temperature in the process.
- Condensation: The hot, pressurized gas flows into the condenser coil, where it releases heat to the surrounding air and condenses into a high-pressure liquid.
- Expansion: The high-pressure liquid refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, which reduces its pressure and temperature as it enters the evaporator coil.
- Evaporation: In the evaporator coil, the cool, low-pressure liquid absorbs heat from the indoor air, turning back into a low-pressure gas in the process.
Circulation of Air
In conjunction with the refrigeration cycle, an air conditioner utilizes fans to circulate and distribute the cooled air throughout the space. Warm air is drawn into the system through return ducts, passes over the evaporator coil to be cooled, and is then pushed back into the room through supply ducts.
Thermostat and Control Systems
Modern air conditioners are equipped with sophisticated thermostat and control systems that regulate the operation of the unit based on the desired temperature settings. These systems ensure that the air conditioner runs efficiently and maintains a comfortable indoor environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the science behind how air conditioners work is a fascinating blend of thermodynamics, heat transfer, and fluid mechanics. By understanding the basic principles of air conditioning, we can better appreciate the ingenuity and engineering that go into keeping us cool during the sweltering summer months.